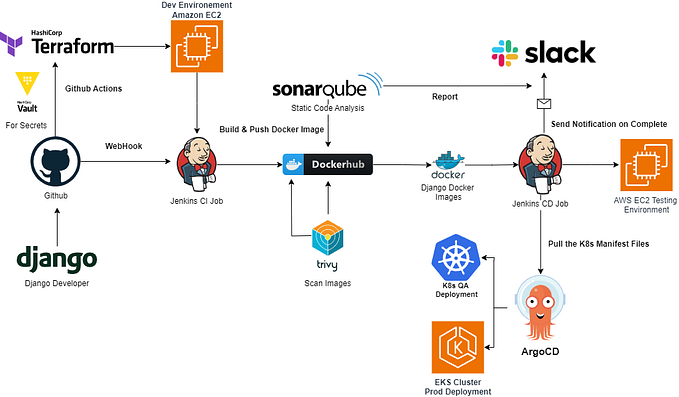
Understanding Apigee Proxy Deployment Automation with GitHub Actions

In today’s API-driven world, managing and deploying API proxies efficiently is crucial for maintaining a robust API infrastructure. This blog post explores a sophisticated GitHub Actions workflow designed for automated Apigee proxy deployment, covering both non-production and production environments with proper security controls and validation steps.
Overview
The workflow implements a comprehensive deployment pipeline for Apigee API proxies, featuring:
- Multi-environment deployment support
- Strong validation and security checks
- Automated build and deployment processes
- Production approval gates
- Detailed deployment verification
Key Features
1. Environment Flexibility
The workflow supports multiple environment groups and types:
- Environment Groups: default, retail, CRM, etc
- Environment Types: dev, test, uat, prod
2. Security Controls
- Workload Identity Federation for secure authentication
- Separate service accounts for production and non-production environments
- Manual approval gate for production deployments
- Environment-specific secrets management
3. Validation and Quality Checks
- API proxy validation using apigeelint
- Environment configuration validation
- Deployment verification steps
- Comprehensive error handling
Workflow Architecture
The deployment process is divided into several key stages, each handling specific aspects of the deployment pipeline. Let’s break down each major component:

Stage 1: Input Validation
The workflow begins with comprehensive validation of all input parameters:
- Environment group and type validation
- Production deployment requirements check
- Configuration compatibility verification
Stage 2: Authentication Setup
- Separate authentication for production and non-production environments
- Uses Google Cloud Workload Identity Federation
- Generates and manages access tokens securely
Stage 3: Build and Validation
- API proxy validation using apigeelint
- Bundle creation and packaging
- Version management and tracking
Stage 4: Non-Production Deployment
- Automated deployment to non-production environments
- Environment-specific configuration application
- Deployment verification and health checks
Stage 5: Production Deployment
- Manual approval requirement
- Production bundle creation and validation
- Staged deployment process
- Post-deployment verification
Best Practices Implemented
1. Security First
— Separate service accounts for different environments
— Secure secret management
— Environment-specific permissions
2. Quality Assurance
— Automated validation checks
— Code quality verification
— Deployment verification steps
3. Error Handling
— Comprehensive error checking
— Detailed logging
— Failure recovery mechanisms
4. Automation
— Minimal manual intervention
— Automated version management
— Consistent deployment process
Implementation Considerations
When implementing this workflow, consider:
1. Setting up proper IAM permissions in Google Cloud
2. Configuring environment secrets in GitHub
3. Setting up appropriate approval processes
4. Customizing validation rules based on organizational requirements
Conclusion
This GitHub Actions workflow provides a robust, secure, and automated approach to managing Apigee proxy deployments. It incorporates industry best practices while maintaining flexibility for different organizational needs. The workflow’s modular nature allows for easy customization and extension based on specific requirements.
Wait for Part 2, Detailed implementation



![Key Observability Trends for 2024 [AI and Opentelemetry(Otel)]](https://miro.medium.com/v2/resize:fit:679/1*Ywks1br3kTY8nC_IM3nB1A.png)